Getting admitted abroad has always been a favourite choice of Indian students after their 12th class. As of 2025, there are 1.3 million more students abroad than in India since 2023. Parents have challenging decisions to make, including weighing cost vs value, comparing quality of education, assessing career opportunities, and considering cultural adaptation. Admission to foreign universities also has unique requirements and challenges, including early planning and a solid understanding of international education systems.
Eligibility & Admission Requirements: India vs Abroad
Admission in foreign universities after 12th has different requirements from Indian institutions. Parents need to know what these differences are so they can make knowledgeable decisions and plan accordingly. For domestic and international schools, there is a difference in admission procedures:
-
Indian College Registration Requirements
Marks in the board examinations are taken as the basic criteria for the selection, while class 12th marks are the eligibility criteria for most undergraduate courses. Entrance examinations like JEE Main for engineering and NEET for medical courses form mandatory components. Category-based reservations provide quotas for SC, ST, OBC, and EWS categories. State-level counselling processes are followed to allocate the seats on a merit and reservation basis. Beyond this, students going for postgraduation also have to appear for PG entrance exams, such as CAT for MBA.
-
International University Requirements
Recognition of the Higher Secondary School Certificate depends upon the country under consideration, but most universities directly recognise the CBSE and ICSE boards. For admission to the US, SAT or ACT scores are required. Language proficiency can be demonstrated through IELTS (minimum 6.5 band) or TOEFL tests. Letters of Recommendation from a teacher or counsellor provide academic endorsements. Statement of Purpose essays showcase your motivation and career aspirations.
-
Documentation for Admission Overseas
Student visa applications require a passport validity of a minimum of six years. Financial documentation proving the ability to cover tuition and living expenses is a must. Medical examinations and vaccination records meet health requirements. Academic transcripts require apostille certification for legal recognition.
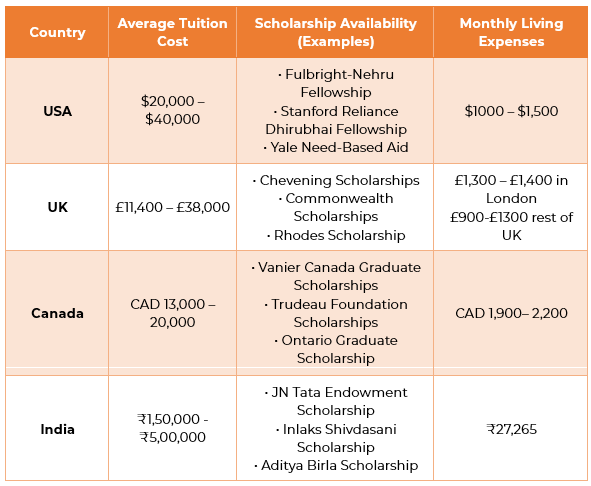
Cost Comparison: Tuition, Living & Scholarships
Financial planning represents the most important factor in deciding between Indian and international education. Admission to study abroad involves higher costs but offers greater scholarship opportunities.
Is It Better To Do Undergraduate Studies In India Or Abroad: Quality of Education, Curriculum & Infrastructure
Undergraduate study in India or abroad depends on education quality, curriculum design, and infrastructure. The Indian market is seen as affordable and familiar, while international universities are seen as providers of exposure to the world and equipped with advanced facilities. Each system has its own advantages:
- Research Infrastructure: International universities spend more on research infrastructure than Indian research institutions. Laboratory equipment gets regular upgrades with the latest technology integration. Faculty research productivity in leading universities worldwide is much higher than Indian counterparts.
- Curriculum Relevance: International programmes update curricula every 2-3 years, incorporating industry developments. Interdisciplinary studies allow the combination of several subjects. Practical learning through internships becomes mandatory in most programmes. To take one example, commerce exams in other countries can cover such subjects as fintech, blockchain usage, or sustainable business practices that are not necessarily available in the curriculum of domestic universities.
- Global Exposure: International classrooms provide some level of cultural mix of students based on their countries of origin. Through an exchange programme, students are given study opportunities for one semester in partner institutions. Industry liaison allows for internships in multinational companies.
Career Prospects & Return on Investment (ROI)
When considering a study abroad admission, students often weigh future career opportunities and the financial value of their degree. International degrees command higher salaries but require initial investment. Career outcome analysis demonstrates returns across education systems:
- Salary Differentials: International graduates command higher starting salaries in developed countries. Graduates from top Indian schools are getting good pay in the home country. The international degree holders returning to India will enjoy the advantage of currency conversion. International education experience is preferred for senior-level positions.
- Degree Recognition: Professional licensing requirements vary by profession and country. Medical degrees awarded by some countries require qualification examinations for practice in India. Engineering degrees issued by Washington Accord member institutions are automatically recognised. An MBA from AACSB business schools is accepted across the world.
- Work Authorisation: Post-study work permits allow you to work for 1-3 years in the graduation country. H1B visa lottery system blocks long-term US jobs for Indians. In Canada, Express Entry programmes offer permanent residency options. The European Union Blue Card allows for skilled worker immigration.
When and How to Start Planning for Admission Abroad
Starting early can make it more likely to be accepted by universities abroad. Ideally, it should start by the 11th standard and have a phased approach that proceeds through well-defined stages.
- Timeline Management: Standardised test preparation would take 6-12 months of study time. University research and shortlisting require an analysis time of 3-6 months. The preparation of the application takes 2-4 months. Planning of finances must start 1-2 years to the expected enrolment.
- Standardised Test Scheduling: SAT tests are administered year-round, with the registration cut-off dates 5 weeks before. IELTS tests happen monthly, with results available within 13 days. Subject-specific tests like SAT Subject Tests require additional preparation time.
- Document Preparation: Academic transcripts need an official certification from the appropriate education boards. The letters of recommendation should be requested 2 to 3 months in advance to allow time for those writing the letters. Statement of Purpose writing is a task that involves multiple drafts and professional revision. The financial records must demonstrate that liquid funds are in existence.
- Research and Comparison: University ranking systems are available as indicators of academic excellence, but they consider multiple factors. Course curriculum analysis ensures alignment of career objectives. Location preferences influence the cost of living and the need for cultural adaptation. For students considering virtual university admission for overseas options, comparing alumni networks becomes even more critical for long-term career development opportunities.
Challenges & Risks Parents Should Be Aware Of
There are risks associated with foreign university admission that need to be taken into account and minimised. The parents should consider potential issues against anticipated benefits:
- Financial Risks: Currency fluctuation impacts overall education costs every year. Unexpected medical expenses can strain family budgets. Economic recession affects the availability of part-time jobs and scholarships. Education loan interest rates flow with the world’s economy.
- Academic Challenges: Credit transfer policies vary between institutions, creating potential loss of academic progress. Degree equivalence recognition creates a barrier to accepting professionals of this track into a given field. Differences in academic standards and requirements need to be overcome within a certain period. These requirements increase in terms of language proficiency along the programme duration.
- Immigration Uncertainties: Any changes in visa policies affect the study and work authorisations. Any shifts in the political climate also determine how the international student is received and treated. Immigration schemes for post-graduation are thus modified depending on what government policies are in place at any given time. Then come changes in documentation requirements, creating compliance challenges.
- Personal and Social Risks: Cultural adaptation difficulties may sometimes reduce academic performance. Homesickness and loneliness can pave the way to mental health issues needing professional intervention. Time zone differences cause emotional stress due to communication barriers with their families. Barriers to social integration reflect on their overall stay at the university.
Conclusion
The choice of Indian or international education involves assessing financial ability, academic goals, career goals, and individual preparedness for cultural adjustment. Admissions abroad offer superior infrastructure, global exposure, and higher career returns, but demand financial investment and cultural adjustment capabilities. Parents must consider their childʻs academic achievement, the financial background of the family, and how well they will adjust to life abroad to decide whether international schooling will suit their child. Early planning, careful research, and realistic expectation setting are the keys to a good outcome from any chosen educational path.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Do all foreign universities require entrance exams like the SAT/ACT for Indian students?
US and Canadian universities require SAT or ACT scores in undergraduate admissions. The European universities directly accept the marks of the 12th standard without extra entrance tests. The Australian institutions need foundation programmes for students who do not qualify directly through the entry criteria. Asian educational institutions, such as the one in Singapore, require particular college entry exams or neighbourhood test results.
- Can Indian students complete their undergraduate studies in India and then pursue a master’s degree abroad in a more affordable way?
The costs of graduate programmes are less than those of undergraduate education overseas. An exceptionally good academic record froma recognised Indian institute improves the prospects for scholarships for a master’s programme. Research assistantships and teaching assistantships provide funding opportunities unavailable to undergraduate students.
- Is studying abroad always better than studying in India?
Field-specific considerations determine optimal education choices, with some disciplines offering better opportunities domestically. Family financial capacity influences long-term benefit realisation from international education investment. Student personality traits affect adaptation success and overall educational experience quality. For many, the real question becomes – is it better to do an undergraduate in India or abroad?, since career objective alignment with the education location creates different outcome scenarios.
- What are some low-cost countries for Indian students to study abroad?
Germany has tuition-free education in state universities with a low semester fee. Eastern European nations such as Poland and the Czech Republic provide quality education at an affordable cost. Nordic countries offer low-cost programmes with excellent infrastructure and support systems.
- Can Indian students get scholarships for foreign universities after Class 12?
Merit scholarships are based on academic performance and can partially to fully cover tuition. Need-based financial aid considers family income levels for assistance determination. Scholarship programmes by the government, such as Fulbright, are offered that cover the living costs. University-based grants focus on students in certain geographical areas or who have certain talents and accomplishments.